The chemistry laboratories are primarily used for sample preparation. The best possible analysis method is selected depending on the issue at hand. And depending on the analysis method, sample preparation will be carried out differently.
For example, for analysis using X-ray fluorescence, the sample is typically first ground, then dried (including loss on ignition) and a glass bead is produced from the anhydrous powder using fusion digestion. The sample prepared in this way is analyzed for its qualitative and quantitative composition using wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry.
Ultrapure water and high-purity acids are required for mass spectrometric analysis with inductively coupled plasma (ICP), among other things. For this purpose, the mass spectrometer for inorganic element analysis is located in these rooms - in combination with laser ablation, depending on the application.
Devices
- Drying ovens
- Muffle ovens
- Carbolite HT furnace (max. T 1815°C)
- Nabertherm ovens up to 1250°C (2x)
- Labconco Freezone freeze dryer (-50°C collector)
- Gelaire LaminAir Class 100 (ISO 4) Safety cabinet (Laminar Flow Cabinet)
- Fume cupboards (digestors)
- MicroMill (ESI, Portland)
- XRF Scientific xrFuse 1 fusion digestion device
- HD Elektronik und Elektrotechnik GmbH VAA-2M, fusion digestion devices
- Subboiling distillation apparatus
- Agilent ICP-MS 7900
Safety cabinet and fume cupboards
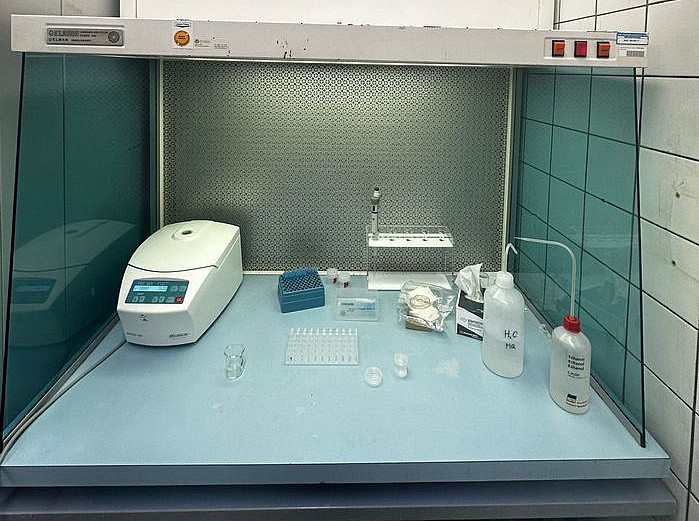
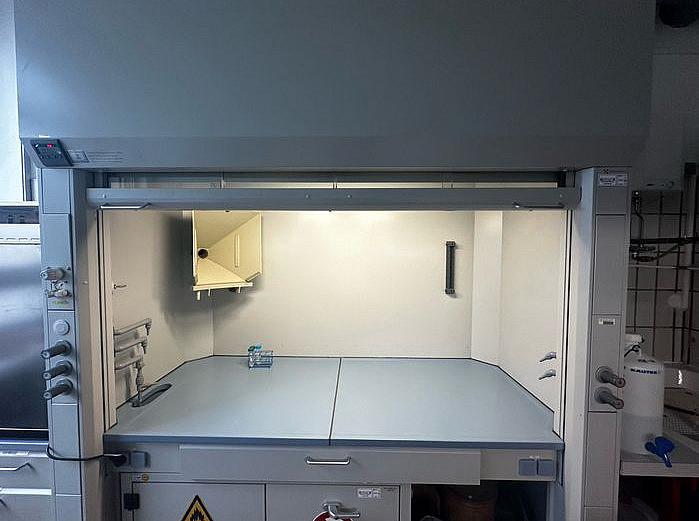
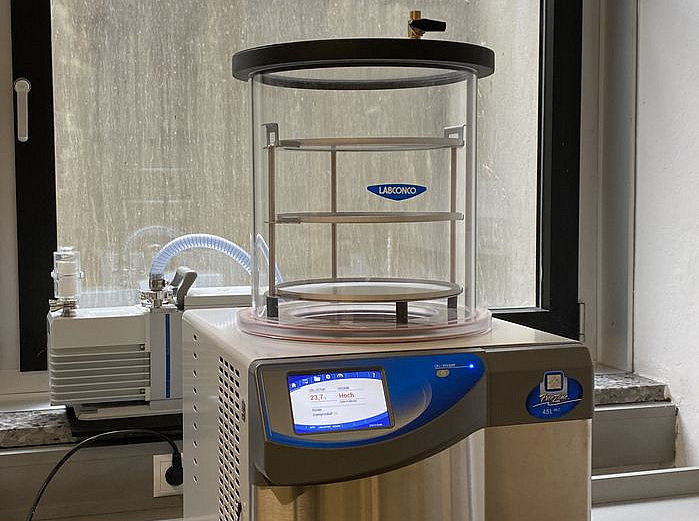



Drying cabinet
The drying ovens are generally used to dry the rock samples so that there is no water left in the sample. To make it easier to compare samples, the analysis data always refer to the dried sample. Drying takes place at 105°C for at least 2 hours.
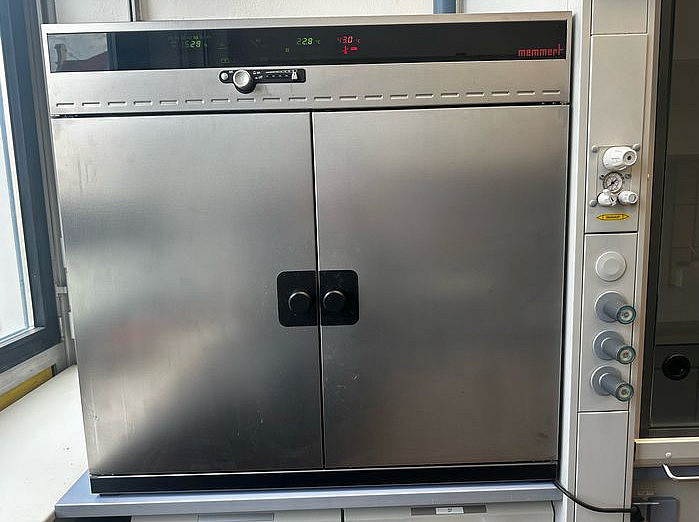
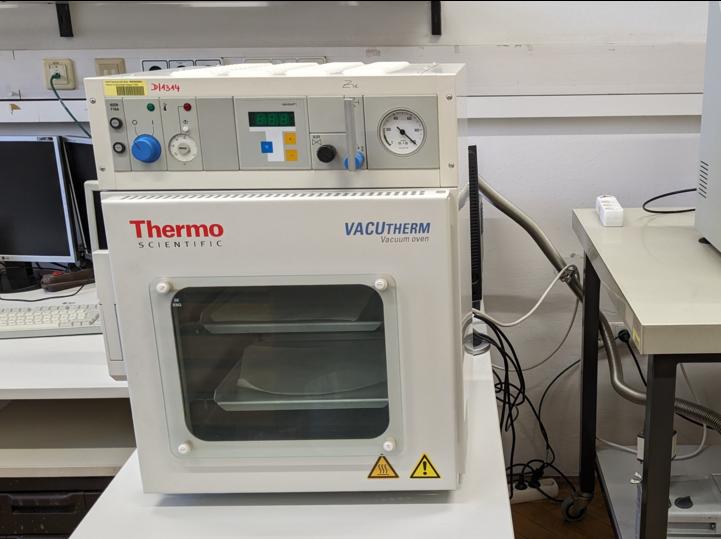
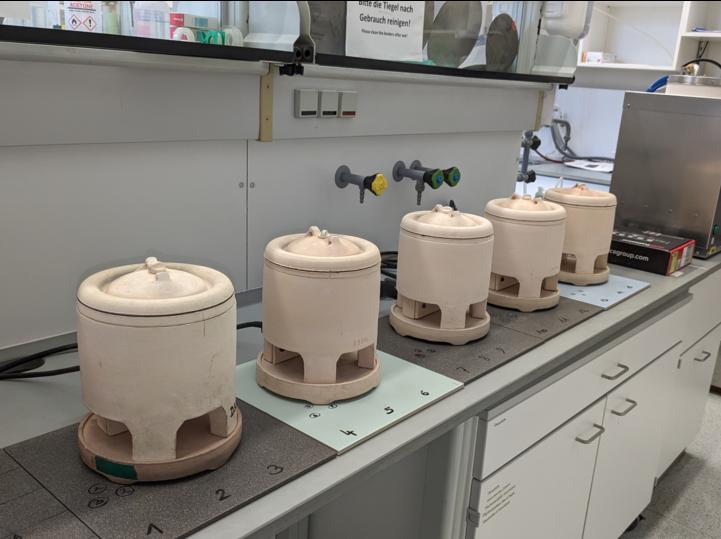



Ovens
The loss on ignition (LOI) of the samples is determined with the aid of muffle furnaces. Determining the loss on ignition is an essential part of X-ray fluorescence analysis. For this purpose, an aliquot of the sample is weighed into a clean porcelain crucible and annealed at 1000°C for 60 minutes. The volatile components of the samples are removed from the sample during this process. After annealing, the crucible cools down in the desiccator (approx. 15-20 minutes) and the sample is weighed.
The loss on ignition (LOI) can be determined on the basis of the weight loss (mass of the sample and the crucible are compared before and after ignition).
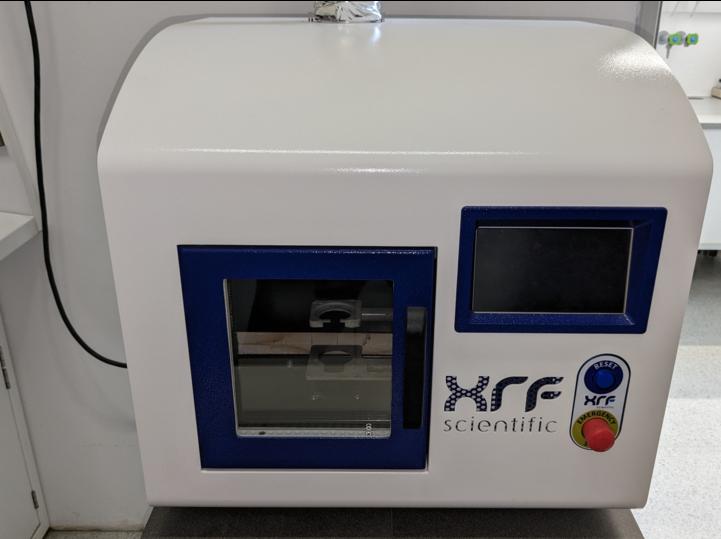

Melt fusion device XRF Scientific xrFuse 1
In a platinum crucible, 1.00 g of sample, 2.38 g of lithium metaborate (LiBO2) and 4.62 g of lithium tetraborate (Li2B4O7) are weighed on the balance. A lithium metaborate-lithium tetraborate mixture is used to lower the melting point of the rock and to be able to break it down.
The crucible together with the sample and a casting dish are placed in the corresponding holders of the electrically operated melting digestion device and the melting process (1150°C) is started. The digestion device automatically rotates the crucible for homogenization during the melting process until the sample is completely melted. The melt is then poured off and cooled in the casting tray until the resulting glass bead has completely hardened.
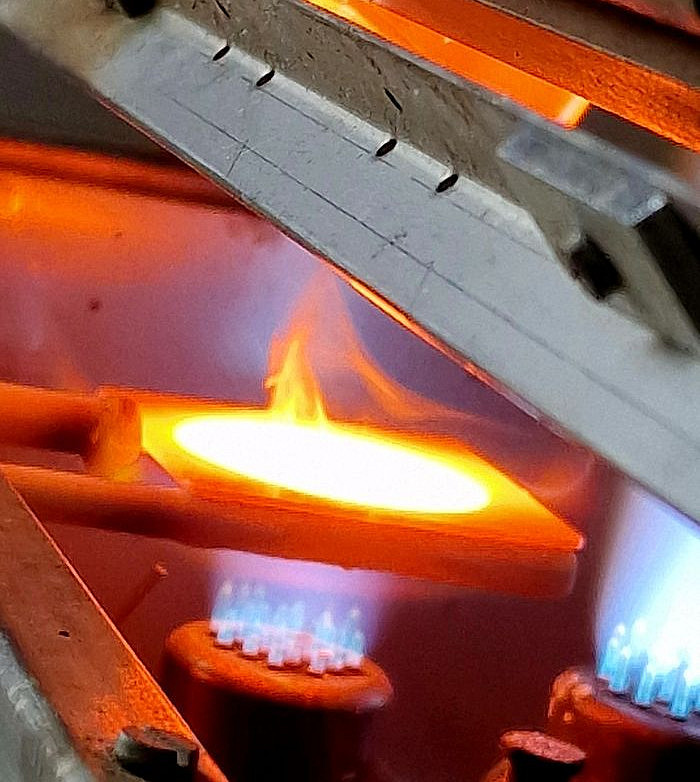
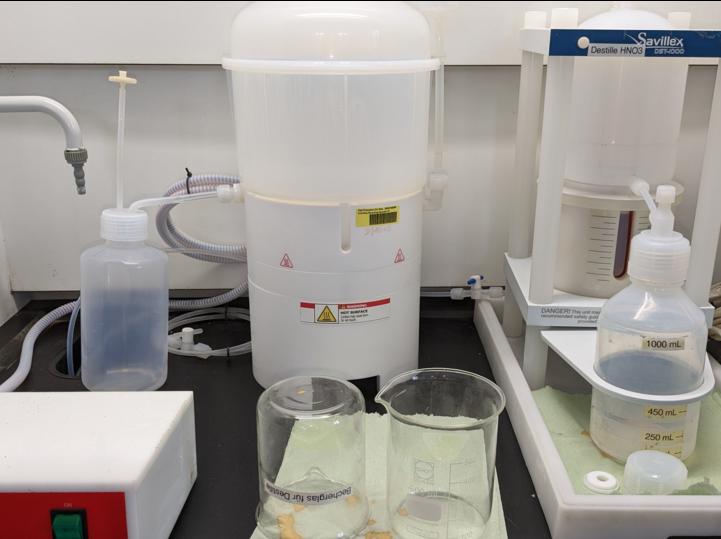

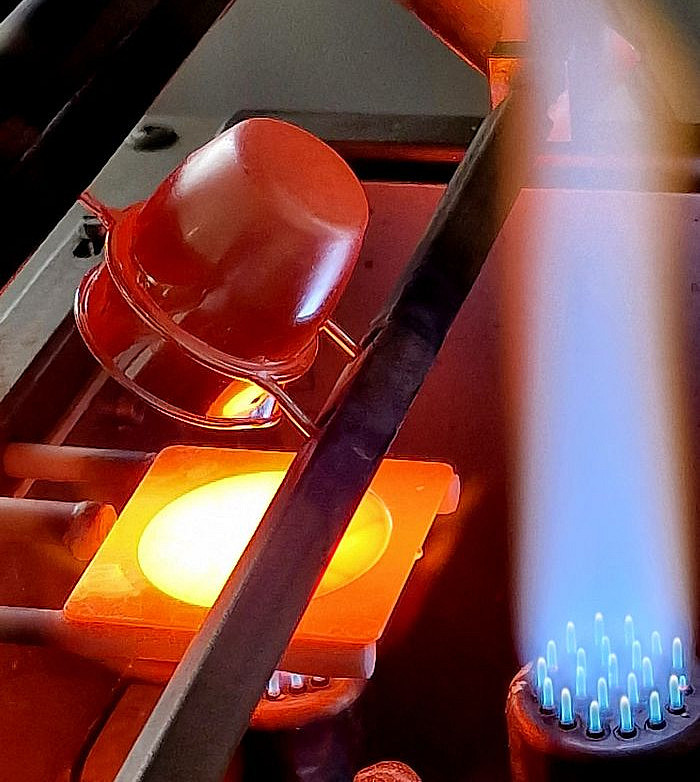

Distillery
The subboiling still is used to purify acids.
Contact us
| +43 316 380 - 8721 Institut für Erdwissenschaften Montag bis Freitag https://erdwissenschaften.uni-graz.at/de/institut-1/ |
| +43 316 380 - 8739 Institut für Erdwissenschaften |
| +43 316 380 - 8724 Institut für Erdwissenschaften |